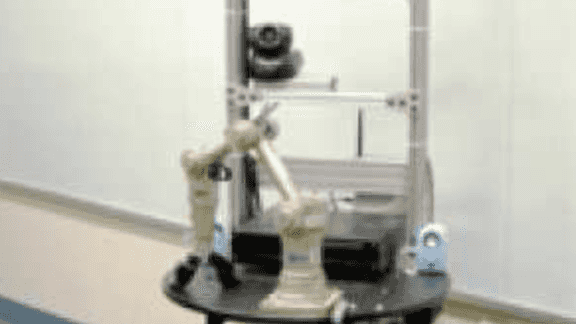
A Vision-Based System for Grasping Novel Objects in Cluttered Environments
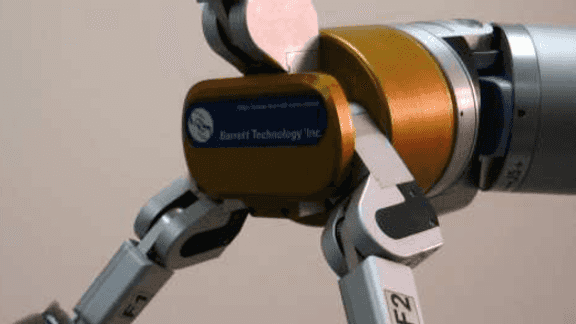
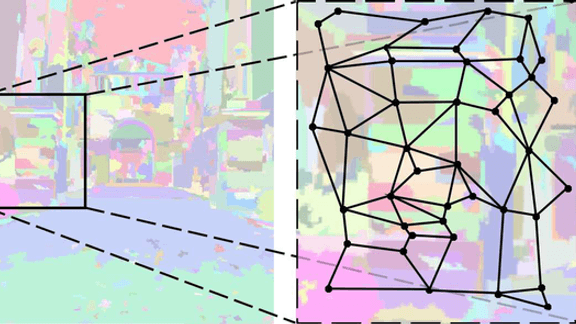
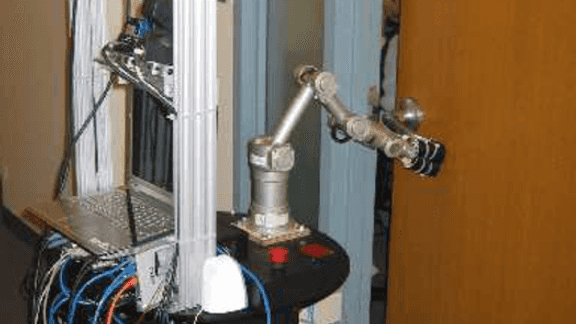
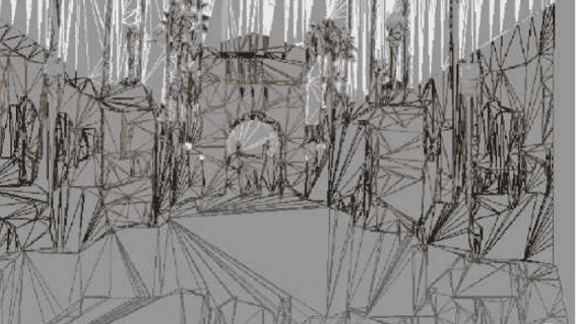
We present our vision-based system for grasping novel objects in clut- tered environments. Our system can be divided into four components: 1) decide where to grasp an object, 2) perceive obstacles, 3) plan an obstacle-free path, and 4) follow the path to grasp the object. While most prior work assumes availability of a detailed 3-d […]